- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance
INTRODUCTION

Menstrual disorders are problems that affect a woman’s normal menstrual cycle. They include painful cramps during menstruation, abnormally heavy bleeding, or not having any bleeding. It occurs during the years between puberty and menopause. Menstruation, also called “menses” or a “period,” is the monthly flow of blood from the uterus through the cervix and out through the vagina.
Menstrual disorders refer to a range of conditions that affect the regular menstrual cycle. These disorders can lead to irregular, heavy, or painful periods, and can significantly impact a person’s overall well-being.
Here are some common types of menstrual disorders:

1.Dysmenorrhea:
. – Dysmenorrhea is characterized by painful cramps before or during menstruation. It can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, fatigue, and lower back pain.
- Menorrhagia:
. – Menorrhagia involves heavy menstrual bleeding that lasts longer than usual. It can lead to the need to change sanitary products frequently, and may result in anemia due to blood loss.
- Amenorrhea:
. – Amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstrual periods. Primary amenorrhea occurs when a person doesn’t start menstruating by the age of 16, while secondary amenorrhea is the absence of periods for six months or more after having regular menstrual cycles.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
. – PCOS is a hormonal disorder characterized by enlarged ovaries with small cysts on the outer edges. It can lead to irregular periods, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
. – PMS and PMDD are characterized by emotional and physical symptoms that occur in the days before menstruation. PMDD symptoms are more severe and can include mood swings, irritability, and depression.
- Endometriosis:
. – Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. It can cause severe pelvic pain, heavy periods, and infertility.
- Fibroids:
. – Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that can lead to heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, and pain.
- Irregular Periods:
. – Irregular periods involve variations in cycle length, which might indicate hormonal imbalances or other underlying conditions.
If you suspect you have a menstrual disorder or experience any abnormal menstrual symptoms, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional. A proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder and its underlying causes and may include lifestyle changes, medication, hormonal therapies, or surgical interventions. Additionally, QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
The Female Reproductive System
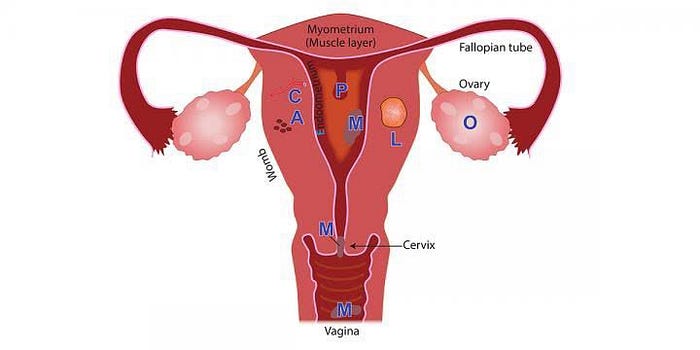
The organs and structures in the female reproductive system include:
- The uterus is a pear-shaped organ located between the bladder and lower intestine.
- The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus. It contains the cervical canal, which connects the uterine cavity with the vagina and allows menstrual blood to drain from the uterus into the vagina. The vaginal opening of the canal is called the external os. Pap smears are collected from the external os.
- The fallopian tubes connect the uterus and ovaries. Ovaries are egg-producing organs that hold 200,000 to 400,000 follicles (from folliculus, meaning “sack” in Latin). These cellular sacks contain the materials needed to produce ripened eggs, or ova. An egg develops within the follicle.
- The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. During pregnancy it thickens and becomes enriched with blood vessels to house and nourish the growing fetus.
- If at the end of a menstrual cycle pregnancy does not occur, the endometrium is shed and the woman starts menstruating. Menstrual flow consists of blood and mucus from the cervix and vagina.
- The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth
CAUSES LEADING TO MENSTRUAL DISORDERS
The causes of menstrual disorders can vary depending on the specific type of disorder. Here are some common factors that can contribute to different menstrual disorders:
1.Dysmenorrhea: The exact cause of primary dysmenorrhea (common menstrual cramps) is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the release of prostaglandins, which cause the uterine muscles to contract. Secondary dysmenorrhea can be caused by conditions like endometriosis or fibroids.
-
Menorrhagia: Hormonal imbalances, such as an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone, can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding. Other factors may include uterine fibroids, polyps, adenomyosis, or bleeding disorders.
-
Amenorrhea: Primary amenorrhea can be caused by developmental issues, genetic conditions, hormone imbalances, or structural abnormalities of the reproductive organs. Secondary amenorrhea can be due to factors like pregnancy, stress, excessive exercise, weight loss, or medical conditions affecting the ovaries or thyroid.
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):PCOS is believed to be linked to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances. It can be genetic and is characterized by high levels of androgens (male hormones) and anovulation (lack of regular ovulation).
-
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD): Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle are thought to contribute to PMS and PMDD. The exact causes are still being studied, but neurotransmitter changes, genetics, and sensitivity to hormone fluctuations might play a role.
-
Endometriosis: The exact cause of endometriosis is not fully understood, but it involves the growth of tissue similar to the uterine lining outside the uterus. It might be related to genetics, hormonal imbalances, and immune system dysfunction.
-
Fibroids: Uterine fibroids are thought to develop due to a combination of genetic factors and hormonal changes. Estrogen is believed to promote their growth.
-
Irregular Periods: Irregular periods can be caused by hormonal imbalances, stress, rapid weight changes, medical conditions affecting the reproductive system, certain medications, or changes in birth control methods.
It’s important to note that these are general factors, and the specific causes can vary from person to person. If you’re experiencing abnormal menstrual symptoms or have concerns about your menstrual cycle, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management. QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
SPOTTING THE SIGNS OF MENSTRUAL DISORDERS

The symptoms of menstrual disorders can vary based on the specific type of disorder. Here are some common symptoms associated with different menstrual disorders:
- Dysmenorrhea (Painful Menstrual Cramps):
. – Severe lower abdominal pain that can radiate to the lower back and thighs.
. – Cramping pain that typically starts before or during menstruation and lasts for hours or even days.
. – Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headaches might accompany the pain.
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding):
. – Menstrual bleeding that lasts longer than seven days.
. – Needing to change sanitary products frequently (more than every two hours).
. – Passing blood clots during menstruation.
. – Fatigue due to excessive blood loss, which can lead to anemia.
- Amenorrhea (Absence of Menstrual Periods):
. – Primary Amenorrhea: Absence of menstruation by age 16 without other development signs.
. – Secondary Amenorrhea: Absence of periods for six months or more after having regular menstrual cycles.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
. – Irregular menstrual cycles or no periods at all.
. – Excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and weight gain.
. – Ovulation-related issues leading to difficulty getting pregnant.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
. – PMS: Emotional symptoms like mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and physical symptoms like bloating and breast tenderness.
. – PMDD: Severe mood swings, depression, irritability, and physical symptoms that significantly interfere with daily life.
- Endometriosis:
. – Severe pelvic pain, especially during menstruation.
. – Painful intercourse, bowel movements, or urination.
. – Infertility issues.
- Uterine Fibroids:
. – Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
. – Pelvic pain or pressure.
. – Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Irregular Periods:
. – Variations in cycle length.
. – Unpredictable bleeding patterns.
. – Spotting between periods.
If you’re experiencing any unusual or disruptive symptoms related to your menstrual cycle, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, perform necessary tests, and provide a proper diagnosis. Treatment options can then be tailored to your specific needs and condition.
TREATING THE TROUBLE
The treatment for menstrual disorders varies depending on the specific type of disorder and its underlying causes. Here are some common treatment approaches for different menstrual disorders:
- Dysmenorrhea (Painful Menstrual Cramps):
. – Over-the-counter pain relievers (NSAIDs) to alleviate cramps and reduce inflammation.
. – Heat therapy, such as using a heating pad, to relieve muscle pain.
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding):
. – Hormonal birth control methods, such as birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or hormone injections, to regulate menstrual bleeding.
. – Non-hormonal medications like tranexamic acid to reduce heavy bleeding.
. – In some cases, surgical procedures like endometrial ablation or hysterectomy might be considered.
- Amenorrhea (Absence of Menstrual Periods):
. – Treatment depends on the underlying cause. For hormonal imbalances, hormonal therapies might be recommended.
. – Addressing lifestyle factors like excessive exercise, stress, or weight changes can help restore regular menstruation.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
. – Lifestyle changes like weight management and regular exercise can help regulate hormones.
. – Hormonal birth control can regulate periods and manage symptoms.
. – Medications like metformin might be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity.
. – Fertility treatments if pregnancy is desired.
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
. – Lifestyle changes including regular exercise, balanced diet, stress reduction, and getting enough sleep.
. – Cognitive-behavioral therapy or counseling to manage emotional symptoms.
. – Medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for severe PMS or PMDD.
- Endometriosis:
. – Pain management with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications.
. – Hormonal therapies to suppress the growth of endometrial tissue.
. – Surgical procedures to remove endometrial tissue or treat adhesions.
- Uterine Fibroids:
. – Monitoring and regular check-ups if fibroids are small and not causing symptoms.
. – Hormonal treatments to regulate bleeding and shrink fibroids.
. – Surgical options include myomectomy (removal of fibroids) or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
- Irregular Periods:
. – Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Hormonal birth control, lifestyle changes, and managing underlying conditions can help regulate periods.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can recommend the most suitable approach based on your specific symptoms, medical history, and overall health. It should be noted that, QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
MEDICATIONS AND MANAGEMENT

Medications can play a significant role in treating various menstrual disorders. Here are some common medications that healthcare professionals might use to manage specific menstrual disorders:
- Dysmenorrhea (Painful Menstrual Cramps):
– Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation associated with cramps.
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding):
. – Hormonal Birth Control: Birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, and other hormonal methods can help regulate menstrual bleeding and reduce heavy flow.
. – Tranexamic Acid: This medication helps reduce heavy bleeding by promoting blood clotting.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
. – Hormonal Birth Control:
Oral contraceptives or other hormonal methods can regulate menstrual cycles and manage PCOS symptoms.
4.– Metformin:
This medication can improve insulin sensitivity and help manage PCOS-related hormonal imbalances.
5.Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs):
- SSRIs, commonly used as antidepressants, can help alleviate mood-related symptoms of PMS and PMDD.
- . – Hormonal Birth Control:
- Oral contraceptives can regulate hormonal fluctuations and reduce symptoms.
6.Endometriosis:
. – Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can help manage pain associated with endometriosis.
. – Hormonal Therapies: Hormonal treatments like birth control pills, GnRH agonists, or progestin therapies can suppress endometrial tissue growth.
7.Uterine Fibroids:
. – Hormonal Therapies: Hormonal birth control or progestin-releasing IUDs can help manage heavy bleeding and shrink fibroids.
. – Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Agonists:These medications can temporarily shrink fibroids by reducing estrogen production.
It’s important to note that medications should be prescribed and managed by a healthcare professional based on your individual condition, medical history, and any other medications you might be taking. They can discuss the benefits, potential side effects, and expected outcomes of specific medications for your menstrual disorder.
PREVENTATIVE MEASURES
While not all menstrual disorders can be prevented, there are steps you can take to promote menstrual health and reduce the risk of certain issues. Here are some preventive measures:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
. – Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support hormonal balance.
. – Engage in regular physical activity to manage weight and promote overall health.
- Manage Stress:
. – Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
. – Chronic stress can affect hormone levels and exacerbate menstrual symptoms.
- Stay Hydrated:
. – Drink plenty of water to support overall bodily functions and keep the body hydrated.
- Birth Control:
. – Hormonal birth control methods can regulate menstrual cycles and manage symptoms of certain disorders.
. – Consult a healthcare professional to determine the best birth control option for you.
- Be Mindful of Intense Exercise:
. – Excessive or intense exercise can sometimes lead to irregular periods or amenorrhea. Balance is key.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
. – Both obesity and being underweight can affect menstrual health. Aim for a healthy weight range.
- Address Underlying Conditions:
. – If you have conditions like PCOS or thyroid issues, work with a healthcare provider to manage them effectively.
- Regular Check-ups:
. – Regular gynecological check-ups can help catch potential issues early and receive appropriate treatment.
- Recognize Your Body’s Signals:
. – Pay attention to changes in your menstrual cycle and symptoms. If something seems off, seek medical advice.
- Prioritize Self-Care:
. – Get sufficient sleep, engage in hobbies you enjoy, and practice self-care to support overall well-being.
It’s important to note that while prevention measures can reduce the risk of certain menstrual disorders, some conditions may still develop due to factors beyond your control. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. They can provide personalized guidance to manage and improve your menstrual health.
CONCLUSION

In conclusion, menstrual disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that can impact the regularity, flow, and overall experience of menstruation. From painful cramps to heavy bleeding and hormonal imbalances, these disorders can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. It’s important to recognize the signs and symptoms of menstrual disorders and seek professional medical guidance for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment.
Each menstrual disorder has its own set of causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in determining the most appropriate treatment plan based on an individual’s unique circumstances. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, over-the-counter pain relievers, hormonal therapies, or other interventions, effective management of menstrual disorders can lead to improved well-being and better quality of life.
Remember that you don’t have to navigate menstrual disorders alone. Seeking medical advice and support is essential to finding the best solutions to manage symptoms and restore menstrual health.
QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer