- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
Introduction
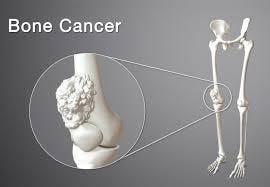
Bone cancer refers to a type of cancer that originates in the bones. It occurs when abnormal cells within the bone tissue begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Bone cancer can either start in the bone itself (primary bone cancer) or spread to the bone from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic bone cancer). Primary bone cancer is rare, and there are several subtypes, including osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, and chondrosarcoma. Metastatic bone cancer is more common and typically occurs as a result of cancer spreading from other parts of the body, such as the breast, lung, or prostate.
Bone cancer can cause pain, weakening of the bone, and other symptoms. Treatment options vary based on factors such as the type of bone cancer, its stage, and the individual’s overall health. Treatments may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. Early detection and appropriate treatment are important for improving outcomes in bone cancer cases.
The diagnosis and treatment of bone cancer involve a combination of medical evaluations, imaging tests, and biopsies to determine the presence of cancer, its type, and its extent. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic process and potential treatment options:
Spotting The Signs Of Bone Cancer
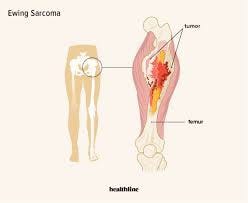
Symptoms of bone cancer can vary depending on factors such as the type of bone cancer, its location, and its stage. Some common symptoms and signs to be aware of include:
-
Pain: Pain in the affected bone is one of the most common symptoms. The pain might initially be intermittent and become more persistent over time. It may worsen at night or with physical activity.
-
Swelling or Lump: A noticeable lump or swelling near the affected bone might be present. This could cause an area of the bone to feel tender or warm to the touch.
-
Fractures: Bone weakened by cancer can be more susceptible to fractures, even from minor injuries or normal activities.
-
Limited Range of Motion: If the tumor is located near a joint, it might restrict movement and cause discomfort.
-
Fatigue: General fatigue and weakness can occur as the body responds to cancer growth.
-
Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss might be a symptom of advanced bone cancer.
-
Fever: In rare cases, bone cancer can lead to fever, particularly if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: If bone cancer has spread to other areas, it might cause symptoms related to those specific areas, such as nausea and vomiting if it has spread to the abdomen.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by various conditions, and their presence doesn’t necessarily indicate bone cancer. However, if you experience persistent or concerning symptoms, especially pain that doesn’t improve with rest, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve outcomes in cases of bone cancer.
Diagnosis:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will start by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination to assess symptoms and any signs of bone abnormalities.
-
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and bone scans can provide detailed images of the bones and help identify any tumors, their size, and their location.
-
Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of tissue from the suspected tumor for laboratory analysis. Biopsies help determine whether the growth is cancerous, its type, and how aggressive it is.
-
Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, including tests for tumor markers, can provide additional information about the presence of cancer and its characteristics.
Staging:
If bone cancer is confirmed, further tests may be conducted to determine the stage of the cancer, which involves assessing whether the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or other parts of the body.
Treatment:
The treatment of bone cancer depends on factors such as the type of bone cancer, its stage, and the individual’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
-
Surgery: Surgery is often the primary treatment for bone cancer. It involves removing the cancerous tumor along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure that all cancer cells are removed.
-
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves using powerful medications to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. It may be used before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor or after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to target any remaining cancer cells.
-
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery or as a primary treatment for certain types of bone cancer.
-
Targeted Therapy: Some advanced bone cancers may be treated with targeted therapies that focus on specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to experimental treatments that are being tested for their effectiveness in treating bone cancer.
The choice of treatment will be determined by a team of healthcare professionals and will depend on the specific characteristics of the cancer. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual’s situation and may involve a combination of approaches. It’s important to discuss treatment options, potential side effects, and long-term implications with the healthcare provider to make informed decisions.
Preventative Measures
Preventing bone cancer involves taking steps to reduce the risk factors that might contribute to its development. While there is no guaranteed way to prevent bone cancer, adopting a healthy lifestyle and being proactive about your health can contribute to overall well-being and potentially lower the risk. Here are some strategies that might help:
-
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute to overall health. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also have a positive impact.
-
Protect Against Radiation: If you have a history of radiation therapy, discuss with your healthcare provider any potential long-term risks and ways to monitor your health.
-
Know Your Family History: If you have a family history of bone cancer or other related conditions, inform your healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and screenings might be recommended.
-
Avoid Harmful Chemicals: If you work in an environment where you’re exposed to potentially harmful chemicals, take appropriate safety measures and follow guidelines to minimize exposure.
-
Promptly Address Bone Health: If you have any bone-related conditions or concerns, such as Paget’s disease, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate management and monitoring.
-
Monitor Symptoms: Be vigilant about your health and pay attention to any unusual symptoms, such as persistent pain, swelling, or unexplained weight loss. If you notice anything concerning, consult a healthcare professional.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Routine medical check-ups can help identify any potential health issues, including bone-related concerns, in their early stages.
It’s important to remember that bone cancer is rare, and most people with risk factors never develop the disease. If you have concerns about your risk or any symptoms, discussing them with a healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance and help determine appropriate steps for prevention and early detection. Additionally, staying informed about bone health and seeking medical attention if you notice any unusual changes can contribute to your overall well-being. To make things more feasible ,QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
Conclusion
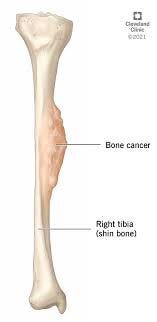
In conclusion, bone cancer is a complex and diverse group of conditions that require vigilance, awareness, and a proactive approach to health. While preventing bone cancer entirely is not always possible, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and promote early detection.
Being attuned to one’s body, recognizing potential symptoms such as persistent pain, swelling, or unexplained changes, and promptly seeking medical attention when needed are all essential practices. Understanding personal risk factors, including family history and previous medical treatments, can guide decisions about preventive measures and regular check-ups.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through a balanced diet, exercise, and weight management can contribute to overall well-being and potentially lower the risk of various health conditions, including bone cancer.
Collaboration with healthcare professionals, regular medical check-ups, and adherence to recommended screenings can aid in identifying potential health concerns in their early stages. If diagnosed, advances in medical technology and treatment options provide hope and positive outcomes for many individuals affected by bone cancer.
Ultimately, while we may not be able to fully prevent bone cancer, we can empower ourselves with knowledge, early detection, and proactive healthcare practices that contribute to living a healthy and fulfilling life.
To Know More QMe,
QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer