- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM
Introduction

Information Hospital Managementmation Systems (HMIS) are integrated software solutions designed to manage various aspects of healthcare facilities. They handle patient data, administrative tasks, financial processes, and clinical operations. HMIS play a crucial role in improving efficiency, patient care, and decision-making within healthcare organizations. They enable better communication between departments, accurate record-keeping, and data analysis, ultimately enhancing overall healthcare service delivery.
A detailed breakdown of the components that make up a Hospital Management Information System (HMIS):
Patient Management:
Patient Registration: This module captures patient demographic details, contact information, medical history, and insurance information. It generates a unique patient identifier.
- Admission and Discharge: Tracks patient admissions, discharges, and transfers within the hospital. It manages bed assignments and helps optimize resource utilization.
- Patient Records: Stores electronic health records (EHRs) containing medical histories, diagnoses, treatment plans, progress notes, and prescriptions.
- Patient Portal: Provides patients with secure access to their medical records, appointment schedules, test results, and treatment plans.
2. Appointment Scheduling:
. Appointment Booking: Allows patients to request appointments online or through the hospital. Staff can manage and schedule appointments, avoiding conflicts and overbooking.
. Calendar Management: Displays available time slots for different healthcare providers, helping front-desk staff efficiently manage patient appointments.
3. Billing and Financial Management:
. Billing and Invoicing: Generates bills for medical services provided, including consultations, procedures, and medications. Invoices can be sent to patients or insurance companies.
. Claims Processing: Handles insurance claims submissions and tracks claim status. It ensures accurate coding and documentation to facilitate timely reimbursements.
. Payment Processing: Manages payment methods, tracks payments received, and provides financial reports. Supports electronic payment options and automates reconciliation.
4. Inventory Management:
. Stock Tracking: Monitors the availability and consumption of medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and equipment. It triggers alerts for low-stock items and automates reordering.
. Supplier Management: Maintains a database of suppliers, manages purchase orders, and tracks deliveries.
. Inventory Reports: Generates reports on stock levels, usage patterns, and expiration dates for effective inventory control.
5. Laboratory and Radiology Integration:
. Test Requests: Enables healthcare providers to request lab tests and radiology procedures electronically.
. Test Result Management: Receives and stores test results in the patient’s electronic health record. Alerts healthcare providers about critical results.
. Imaging Management: Stores medical images like X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasounds. Radiologists can review and interpret images remotely.
6. Electronic Health Records (EHRs):
. Patient Information: Stores comprehensive patient information, including medical history, diagnoses, allergies, medications, and surgical history.
. Clinical Notes: Captures healthcare provider notes during patient visits, facilitating continuity of care among different providers.
. Lab and Imaging Results: Integrates test results and medical images directly into the EHR, providing a complete patient profile.
7. Clinical Decision Support:
. Alerts and Reminders: Notifies healthcare providers of drug interactions, allergies, and recommended preventive screenings.
. Clinical Guidelines: Offers evidence-based treatment recommendations and protocols to aid medical decision-making.
8. Reporting and Analytics:
. Performance Metrics: Generates reports on patient demographics, treatment outcomes, revenue, and expenses for strategic planning.
. Data Visualization: Presents data in graphical formats, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
. Predictive Analytics: Uses historical data to forecast patient admission rates, resource utilization, and staffing needs.
These components collectively form a comprehensive Hospital Management Information System, contributing to efficient healthcare delivery, patient satisfaction, and improved clinical outcomes.
Significance Of Hospital Management Information System
The significance of Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS) in healthcare cannot be overstated. Here are some key reasons why HMIS are highly significant:
-
Enhanced Patient Care: HMIS provide healthcare professionals with quick access to accurate patient records, medical history, and diagnostic results. This leads to more informed decision-making, personalized treatments, and improved patient outcomes.
-
Streamlined Workflows: By automating administrative tasks, appointment scheduling, and record-keeping, HMIS simplify and optimize healthcare operations. This reduces manual errors, saves time, and allows staff to focus on patient care.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: HMIS generate detailed reports and analytics on various aspects of healthcare operations. These insights help hospital administrators and managers make informed decisions about resource allocation, staff distribution, and facility expansion.
-
Efficient Resource Management: HMIS assist in managing hospital resources such as beds, equipment, and staff. This ensures efficient utilization, reduces wait times, and enhances patient satisfaction.
-
Improved Communication: Different departments within a healthcare facility can share patient information seamlessly through HMIS. This fosters better communication among healthcare providers, leading to coordinated care.
-
Data Security and Privacy: HMIS incorporate robust security measures to safeguard sensitive patient data. They ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA, protecting patient privacy and confidentiality.
-
Reduced Paperwork: The transition from paper-based records to electronic systems minimizes paperwork, reducing administrative burdens, and decreasing the risk of errors caused by manual data entry.
-
Remote Access: Authorized healthcare professionals can access patient records remotely, enabling telemedicine consultations, remote diagnostics, and collaborative care even outside the hospital premises.
-
Accurate Billing and Claims: HMIS automate billing processes, ensuring accurate invoicing and timely claims submissions to insurance companies. This accelerates payment processing and minimizes revenue leakage.
-
Support for Research and Analysis: Aggregated data within HMIS can be anonymized and used for medical research, clinical trials, and epidemiological studies, contributing to advancements in medical science.
-
Training and Education: HMIS can be used as educational tools for medical students and trainees to understand real-world patient cases, treatment approaches, and medical records management.
-
Disaster Recovery: Electronic records within HMIS are less susceptible to physical damage or loss compared to paper records. This makes disaster recovery and data backup easier to manage.
In summary, HMIS revolutionize the way healthcare facilities operate by integrating various functions, promoting efficient communication, and ensuring accurate data management. They ultimately lead to improved patient care, operational efficiency, and informed decision-making in the healthcare industry.
HMIS Impact In Today’s World.
In today’s world, Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS) have evolved significantly to keep up with technological advancements and the changing needs of the healthcare industry. Here are some ways HMIS are being utilized in the current landscape:
-
Cloud-Based Solutions: Many HMIS are now offered as cloud-based platforms, allowing healthcare organizations to access and manage patient data securely from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly useful for telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
-
Interoperability: HMIS are designed to facilitate interoperability, allowing different healthcare systems and software to communicate and share patient data seamlessly. This enables a holistic view of patients’ medical history, regardless of the healthcare facility they visit.
-
Mobile Applications: Mobile apps integrated with HMIS empower healthcare providers to access patient records, update information, and communicate with colleagues on the go. Patients can also access their medical records and schedule appointments through mobile apps.
-
Data Analytics and AI: HMIS are increasingly incorporating data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. These technologies help in identifying trends, predicting disease outbreaks, optimizing resource allocation, and providing personalized patient care.
-
Telemedicine Integration: HMIS play a crucial role in facilitating telemedicine services. They enable virtual consultations, secure video conferencing, and the exchange of medical information between patients and healthcare providers.
-
Patient Engagement: Modern HMIS often include patient engagement features such as online portals, where patients can view their medical records, schedule appointments, and communicate with healthcare providers directly.
-
Cybersecurity Measures: With the growing concern about data breaches, HMIS are designed with robust cybersecurity features to ensure patient data remains confidential and secure.
-
Personalized Medicine: HMIS aid in delivering personalized healthcare by aggregating patient data and providing insights that enable healthcare providers to tailor treatments based on individual patient characteristics.
-
Population Health Management: HMIS are used to analyze large sets of patient data to identify health trends within specific populations. This data-driven approach helps in designing targeted interventions and preventive strategies.
-
Digital Imaging Integration: HMIS seamlessly integrate with digital imaging systems like PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) to store and manage medical images, facilitating quick access for diagnosis and treatment planning.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Given the increasing emphasis on data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, modern HMIS are designed to ensure compliance with these regulations, safeguarding patient data.
-
Remote Monitoring and Wearables: HMIS can connect with wearable health devices, collecting real-time health data and sending alerts to healthcare providers in case of abnormal readings.
In today’s fast-paced healthcare landscape, HMIS continue to play a critical role in improving patient care, optimizing operational efficiency, and facilitating the adoption of digital technologies for better healthcare outcomes.
A STEP CLOSER TO DIGITAL WORLD: HMIS
Certainly, Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS) offer numerous advantages that significantly impact healthcare organizations and patient care. Here are some key advantages:
-
Enhanced Patient Care: HMIS provide healthcare professionals with quick access to comprehensive patient records, allowing for accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
-
Efficient Workflow: By automating administrative tasks, appointment scheduling, and record-keeping, HMIS streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and save time, enabling staff to focus on patient care.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: HMIS generate detailed reports and analytics that assist hospital administrators and managers in making informed decisions about resource allocation, staffing, and service improvement.
-
Improved Communication: Different departments within a healthcare facility can share patient information seamlessly through HMIS, leading to better coordination of care and smoother operations.
-
Resource Optimization: HMIS help manage resources like beds, equipment, and staff efficiently, reducing wait times, improving patient flow, and enhancing overall resource utilization.
-
Data Security and Privacy: HMIS incorporate robust security measures to protect patient data, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, and safeguarding patient privacy.
-
Reduced Paperwork: The shift from paper-based records to electronic systems minimizes administrative overhead, reduces the risk of errors, and contributes to a more eco-friendly approach.
-
Remote Access: Authorized healthcare professionals can access patient records remotely through HMIS, allowing for telemedicine consultations, remote diagnostics, and collaborative care.
-
Accurate Billing and Claims: HMIS automate billing processes, reducing billing errors and enabling timely claims submissions, which accelerates payment processing and revenue management.
-
Support for Research and Analysis: Aggregated data within HMIS can be used for medical research, clinical trials, and epidemiological studies, leading to advancements in medical science.
-
Educational Tools: HMIS can serve as valuable educational tools for medical students and trainees, offering real-world patient cases and records for learning purposes.
-
Disaster Recovery: Electronic records in HMIS are less susceptible to damage or loss compared to paper records, making disaster recovery and data backup more manageable.
-
Telemedicine Integration: Many HMIS facilitate telemedicine services, enabling virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and better accessibility to healthcare services.
-
Personalized Medicine: HMIS assist in delivering personalized healthcare by aggregating patient data and providing insights that enable tailored treatments based on individual patient characteristics.
-
Population Health Management: HMIS analyze large datasets to identify health trends within specific populations, helping design targeted interventions and preventive strategies.
-
Digital Imaging Integration: HMIS seamlessly integrate with digital imaging systems for storing and managing medical images, allowing quick access for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Overall, HMIS play a pivotal role in improving patient care quality, operational efficiency, data security, and informed decision-making in healthcare organizations. In today world, there are many software that are providing services at HMIS, one of them being QMe: A Healthcare Management Information System. Click on the link to know more about QMe.
DISADVANTAGES
While Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS) offer significant advantages, there are also some potential disadvantages and challenges associated with their implementation. Here are a few:
-
Initial Costs: Implementing an HMIS involves significant upfront costs, including software development, hardware setup, training, and data migration. Small healthcare organizations might find these costs prohibitive.
-
Complex Implementation: HMIS implementation is often complex and requires careful planning and execution. Integrating the system with existing processes and workflows can be challenging and time-consuming.
-
Staff Training: Transitioning to an HMIS requires staff to learn new software and processes. Training can be time-consuming and might lead to reduced productivity during the learning curve.
-
Resistance to Change: Healthcare professionals accustomed to traditional paper-based systems might resist transitioning to digital systems, leading to resistance and decreased efficiency during the transition phase.
-
Technical Issues: Technical glitches, system crashes, or downtime can disrupt healthcare operations, affecting patient care and causing frustration among staff.
-
Data Security Concerns: Storing sensitive patient information electronically can raise concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is essential to prevent data leaks.
-
Data Migration Challenges: Transferring existing paper records to electronic format can be challenging and time-consuming. Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of transferred data is crucial.
-
Vendor Lock-In: Once an HMIS is implemented, healthcare organizations might become dependent on the chosen vendor for updates, maintenance, and support. Switching vendors can be difficult.
-
Lack of Standardization: Different HMIS might use different data formats and standards, making data sharing and interoperability between systems from different vendors challenging.
-
User Interface Issues: If the user interface of the HMIS is not intuitive or user-friendly, it can lead to difficulties in data entry and retrieval, causing frustration for healthcare professionals.
-
Loss of Personal Touch: An overreliance on technology can lead to reduced face-to-face interactions between healthcare providers and patients, potentially impacting patient satisfaction.
-
Limited Access in Remote Areas: In regions with limited internet connectivity or technological infrastructure, implementing and using HMIS effectively can be challenging.
-
Maintenance and Updates: Regular maintenance and software updates are necessary to keep the HMIS functioning optimally. Failure to do so can lead to outdated software and security vulnerabilities.
-
Workflow Disruption: During the transition to an HMIS, workflows might be disrupted, affecting the efficiency of healthcare services and potentially leading to patient dissatisfaction.
-
Data Entry Errors: While HMIS reduce manual errors, data entry mistakes can still occur, affecting the accuracy of patient records and potentially impacting patient care.
-
Unintended Consequences: Automating certain processes might lead to unintended consequences or errors if not carefully monitored and managed.
HMIS offer numerous benefits, their implementation and use come with potential challenges and disadvantages. These challenges can often be mitigated with careful planning, training, and ongoing support to ensure that the system aligns with the needs and goals of the healthcare organization. While many Organisations have disadvantages when it comes to QMe it offers numerous benefits to HMIS.
QMe: A HEALTHCARE SYSTEM THAT IS CHANGING LIVES FOR GOOD.

QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
Conclusion
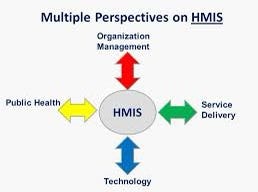
In conclusion, Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS) are indispensable tools that have transformed the healthcare landscape by integrating technology into various aspects of healthcare administration and patient care. These systems offer a multitude of advantages, such as enhanced patient care through accurate records, streamlined workflows, data-driven decision-making, and improved communication among healthcare professionals. They optimize resource management, reduce paperwork, and contribute to better patient outcomes.
However, the implementation of HMIS is not without its challenges. Initial costs, complex implementation, staff training, and concerns about data security are factors that healthcare organizations must carefully navigate. Technical issues, data migration challenges, and potential resistance to change also underscore the need for a thoughtful transition process.
Despite these challenges, the ongoing evolution of HMIS continues to address these issues, incorporating cloud-based solutions, mobile applications, data analytics, and cybersecurity measures. With these advancements, HMIS are better equipped to cater to the demands of modern healthcare, including telemedicine integration, personalized medicine, and improved patient engagement.
As the healthcare industry continues to embrace digital transformation, the significance of HMIS remains evident. These systems empower healthcare organizations to deliver higher quality care, optimize operations, and adapt to the ever-changing landscape of healthcare, ultimately contributing to better patient experiences and improved healthcare outcomes.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer