- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
INTRODUCTION

A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within the brain or its surrounding tissues. Tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can arise from various types of cells in the brain. These growths can interfere with normal brain functions and lead to a range of symptoms, depending on their size, location, and type. Treatment options for brain tumors include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies, which are chosen based on the tumor’s characteristics and the patient’s overall health.
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS INVOLVED
Here are some causes and risk factors that may lead to Brain Tumor,
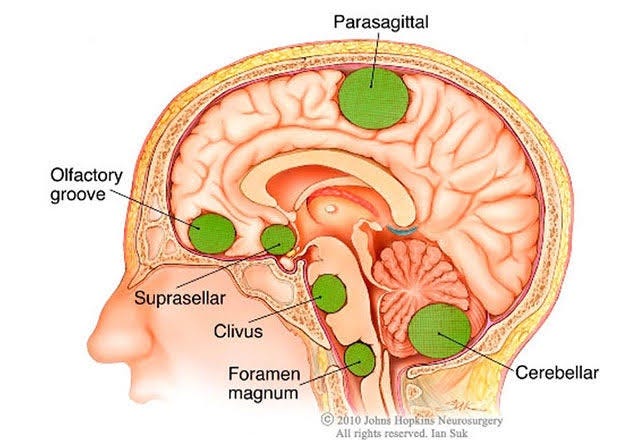
-
Genetic Factors: Some brain tumors have been linked to genetic mutations that can be inherited from family members. Certain hereditary conditions, such as neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2, von Hippel-Lindau disease, and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, are associated with a higher risk of developing brain tumors.
-
Ionizing Radiation: Exposure to high doses of ionizing radiation, such as radiation therapy used to treat other cancers, especially during childhood, can increase the risk of brain tumors. This is more common with radiation exposure at a young age.
-
Hereditary Conditions: Inherited genetic mutations can predispose individuals to brain tumors. For instance, people with neurofibromatosis type 1 have a higher risk of developing optic nerve gliomas, while those with neurofibromatosis type 2 are more prone to developing acoustic neuromas.
-
Environmental Factors: Some studies have suggested a possible link between certain environmental factors and brain tumors. However, these associations are not always well-established. Exposure to certain chemicals, electromagnetic fields, and mobile phone radiation have been investigated, but the evidence is inconclusive.
-
Age: Brain tumors can occur at any age, but certain types are more common in specific age groups. For example, medulloblastomas are often diagnosed in children, while gliomas are more common in adults.
-
Immune System Factors: The immune system plays a role in controlling abnormal cell growth. Some researchers are investigating how immune system dysfunction might contribute to the development of brain tumors.
-
Cellular Changes: Brain tumors can arise from different types of cells within the brain, such as glial cells and neurons. Mutations or changes in these cells’ DNA can lead to uncontrolled growth and tumor formation.
-
Unknown Causes: In a significant number of cases, the exact cause of a brain tumor remains unknown. This underscores the complexity of tumor development and the need for ongoing research to better understand the underlying mechanisms.
It’s important to note that brain tumors are complex and multifactorial, often resulting from a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and chance events at the cellular level. Researchers continue to study these factors to improve our understanding of brain tumor development and potentially develop better prevention and treatment strategies.
SPOTTING THE SIGNS OF BRAIN TUMOUR
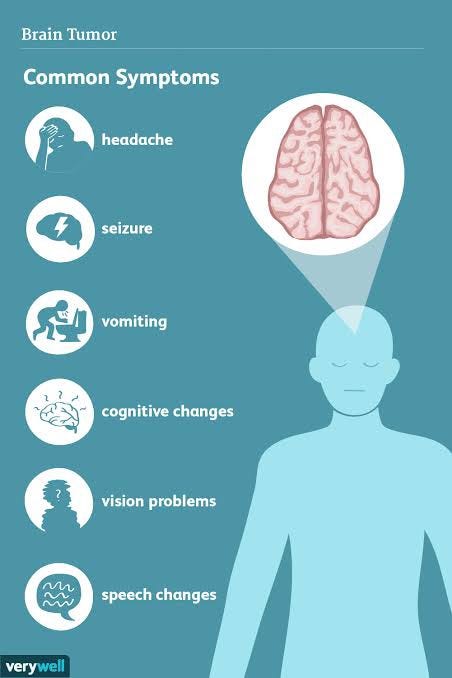
The symptoms of a brain tumor can vary widely depending on the tumor’s size, location, and type. Common symptoms may include:
-
Headaches: Persistent or worsening headaches, especially in the morning or accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
-
Seizures: Unexplained seizures, particularly if they start in adulthood.
-
Cognitive Changes: Memory problems, confusion, difficulty concentrating, and changes in judgment or reasoning.
-
Motor Issues: Weakness, numbness, or tingling in the arms or legs, difficulty walking, and problems with coordination.
-
Sensory Changes: Changes in sensation, such as loss of smell or taste, hearing difficulties, or blurred or double vision.
-
Personality or Mood Changes: Sudden mood swings, irritability, depression, or personality changes.
-
Speech and Language Problems: Trouble speaking, slurred speech, or difficulty understanding speech.
-
Balance and Coordination Issues: Problems with balance, dizziness, and trouble coordinating movements.
-
Vision Changes: Visual disturbances, including blurred vision, loss of peripheral vision, and seeing flashing lights or spots.
-
Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue or drowsiness, even after a good night’s sleep.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Persistent nausea and vomiting, often unrelated to other digestive issues.
-
Changes in Sensation: Changes in the sense of touch, taste, or smell.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by conditions other than brain tumors. However, if you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, especially if they are new or worsening, it’s important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and intervention can greatly improve outcomes for individuals with brain tumors.
RADIATION THERAPY AND CHEMOTHERAPY
Certainly, let’s discuss radiation therapy and chemotherapy as treatment options for brain tumors:
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, involves the use of high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors. It can be delivered externally or internally. In the case of brain tumors:
. External Beam Radiation: This is the most common form of radiation therapy. It involves targeting the tumor from outside the body using a machine that directs focused radiation beams at the tumor. This treatment is carefully planned to minimize damage to healthy surrounding tissue.
. Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Despite the name, this is not a surgical procedure. It’s a precise form of radiation therapy that delivers a high dose of radiation to a specific area of the brain in a single session or a few sessions. It’s often used for smaller tumors or lesions.
. Brachytherapy: In some cases, radioactive material is placed directly into or near the tumor. This is less common in brain tumors compared to other types of cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill or inhibit the growth of cancer cells. However, the effectiveness of chemotherapy in treating brain tumors can be limited due to the blood-brain barrier, which can prevent some drugs from reaching the tumor in sufficient quantities. Nonetheless, chemotherapy can be used in certain situations:
. Systemic Chemotherapy: Drugs are administered orally or through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body, including the brain. Some types of brain tumors are more responsive to systemic chemotherapy.
. Intra-arterial Chemotherapy: In this approach, chemotherapy drugs are delivered directly into the arteries that supply blood to the tumor. This can help bypass the blood-brain barrier to some extent.
. Chemotherapy for Certain Tumor Types: Certain brain tumors, such as medulloblastomas and germ cell tumors, are more sensitive to chemotherapy and may respond well to treatment.
It’s worth noting that the choice of treatment depends on factors like the type and location of the tumor, the patient’s overall health, and whether the tumor is benign or malignant. Often, a combination of treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, is used to effectively manage brain tumors. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual patient’s needs and circumstances.
PREVENTATIVE MEASURES
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent brain tumors, there are some general steps you can take that might help reduce the risk or catch them early:
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper sleep can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of certain health conditions, including some that might contribute to brain tumor development.
-
Protective Measures: If you work in an environment with potential exposure to radiation or harmful chemicals, make sure to follow safety guidelines and wear appropriate protective gear.
-
Avoiding Radiation Exposure: Minimize unnecessary exposure to ionizing radiation. If you need medical imaging tests that use radiation (such as X-rays and CT scans), discuss the benefits and risks with your healthcare provider.
-
Avoiding Harmful Chemicals: Be aware of potential exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins. While the link between specific environmental exposures and brain tumors is not always clear, reducing exposure to harmful substances is generally a good practice.
-
Regular Health Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help detect any potential health issues early, including brain tumors. If you notice any unusual symptoms, discuss them with your healthcare provider.
-
Genetic Counseling: If you have a family history of certain hereditary conditions associated with an increased risk of brain tumors, genetic counseling can provide insights and guidance on managing your risk.
-
Protection from Head Injuries: Some studies have suggested a link between repeated head injuries and certain types of brain tumors. Taking precautions to prevent head injuries, such as wearing helmets during sports and activities with a risk of falls, can be beneficial.
-
Early Detection: Pay attention to any persistent or unusual symptoms, especially those mentioned earlier, and seek medical attention if needed. Early detection and diagnosis can lead to better treatment outcomes.
-
Personal and Family History: Be aware of your personal and family medical history. Certain hereditary conditions can increase the risk of brain tumors. Discuss your medical history with your healthcare provider.
It’s important to remember that brain tumors are complex and can develop for various reasons, some of which might not be preventable. These prevention steps can contribute to overall health and well-being, but they cannot guarantee the complete avoidance of brain tumors. If you have concerns about your risk or are experiencing symptoms, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and recommendations. To make things more feasible, QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, brain tumors are intricate and often unpredictable growths that can profoundly impact an individual’s life. While the causes of brain tumors remain multifaceted and, in many cases, unknown, understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments is crucial.
Early detection of brain tumors is paramount, as it can lead to more effective treatment and better quality of life. Being aware of the common symptoms, such as persistent headaches, seizures, cognitive changes, and sensory disturbances, can prompt timely medical attention.
Treatment options, ranging from surgery and radiation therapy to chemotherapy and targeted therapies, offer hope for managing brain tumors. The approach taken depends on various factors, including the tumor’s type, location, and the patient’s overall health.
While preventing brain tumors entirely is a complex challenge, adopting a healthy lifestyle, minimizing exposure to potential risk factors, and being proactive about medical check-ups can contribute to overall well-being and increase the chances of early detection.
In the face of the unknown, continued research and medical advancements remain essential in enhancing our understanding of brain tumors and refining treatment strategies. By staying informed and collaborating closely with medical professionals, individuals can navigate the complexities of brain tumors with greater resilience and hope for a brighter future.
To Know More About Qme,
QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
10
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer