- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA
INTRODUCTION

Vulvodynia (vul-voe-DIN-e-uh) is a medical term used to describe chronic pain or discomfort in the vulva, which is the external female genitalia. The pain may be described as burning, stinging, or sharp, and it can occur without any identifiable cause. Vulvodynia can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and may require medical evaluation and treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, it’s essential to seek help from a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
CAUSES LEADING TO VULVODYNIA
The exact causes of vulvodynia are not fully understood, and it may vary from person to person. However, several factors have been suggested to contribute to the development of vulvodynia. Here are some of the potential causes:
-
Nerve Abnormalities: Abnormal nerve growth or function in the vulvar region may lead to increased pain sensitivity, making the area more prone to pain and discomfort.
-
Muscle Spasm: Pelvic floor muscle tension or spasms can cause pain in the vulvar area. These spasms may result from factors such as chronic stress, anxiety, or past trauma.
-
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially estrogen, can impact the vulvar tissue’s health and sensitivity.
-
Infections or Inflammation: Previous infections or chronic inflammation in the vulvar area may contribute to vulvodynia.
-
Allergies or Irritants: Some women may have sensitivities or allergies to certain chemicals, soaps, or fabrics that can trigger vulvar pain.
-
Injury or Trauma: Physical trauma, such as previous surgery or injury to the vulvar region, could lead to persistent pain.
-
Genetic Predisposition: There may be a genetic component that increases the risk of developing vulvodynia.
-
Psychological Factors: Emotional stress, anxiety, or a history of sexual trauma can influence pain perception and contribute to vulvodynia symptoms.
It is important to note that the causes of vulvodynia can be complex, and in some cases, multiple factors may be involved.For the most current information, it is recommended consulting a healthcare professional or referring to reputable medical sources. Keeping that in mind,QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
SPOTTING THE SIGNS: VULVODYNIA

The symptoms of vulvodynia are as follows-
- Persistent Vulvar Pain:
The primary symptom of vulvodynia is ongoing pain or discomfort in the vulvar region, which is the external female genital area. This pain may range from mild to severe and can be described as burning, stinging, rawness, itching, soreness, aching, throbbing, or sharp.
- Pain during Sexual Intercourse (Dyspareunia):
Many individuals with vulvodynia experience pain during sexual intercourse. The pain can occur before, during, or after intercourse and can lead to a decrease in sexual desire and activity.
- Pain with Tampon Use:
Inserting and removing tampons may also cause pain or discomfort for some individuals with vulvodynia.
- Pain during Daily Activities:
Vulvodynia can make everyday activities, such as sitting, exercising, or wearing tight clothing, painful and uncomfortable.
- Increased Sensitivity to Touch:
The vulvar area may become more sensitive to touch, leading to discomfort with even gentle pressure.
- Redness or Swelling:
In some cases, the vulva may appear red and swollen, although this symptom is not always present.
- Localised or Generalised Symptoms:
Vulvodynia can affect specific areas of the vulva or be more widespread, involving the entire genital area.
- Chronic Nature:
The pain associated with vulvodynia is typically chronic, lasting for an extended period, often lasting for several months or even years.
- Impact on Quality of Life:
The pain and discomfort can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to emotional distress, anxiety, and interference with daily activities, work, and relationships.
It’s important to remember that the symptoms and their severity can vary from person to person. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation and support from a healthcare professional specialising in women’s health or gynaecology. Proper diagnosis and management can help alleviate the symptoms and improve overall well-being. Additionally, QMe offers package support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
TREATING THE TROUBLE
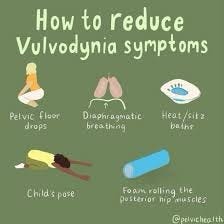
n
The treatment for vulvodynia aims to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Since the exact cause of vulvodynia is not always clear, treatment may involve a combination of approaches. Here are some common treatment options:
- Topical Medications:
Prescription creams or ointments containing local anesthetics, steroids, or other medications can be applied directly to the vulvar area to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Oral Medications:
Pain relievers, tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and certain medications targeting nerve pain (e.g., gabapentin) may be prescribed to help manage chronic pain.
- Physical Therapy:
Pelvic floor physical therapy can be beneficial for women with vulvodynia, especially if muscle tension or spasms contribute to the pain. Techniques like biofeedback and relaxation exercises can be employed.
- Nerve Blocks:
In some cases, nerve blocks may be used to temporarily block pain signals to the vulvar area.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
Avoiding irritants, such as certain soaps or tight-fitting clothing, can help reduce discomfort. Additionally, stress management techniques may be recommended, as stress can exacerbate symptoms.
- Hormone Therapy:
For some women, hormonal treatments, such as topical estrogen creams or hormone replacement therapy, may be helpful if hormonal imbalances contribute to the condition.
- Counseling or Therapy:
Emotional support and counseling can be valuable in managing the emotional impact of vulvodynia, especially if there are psychological factors involved.
- Surgery:
In rare cases where other treatments have been unsuccessful, surgery may be considered as a last resort to remove affected tissue or address nerve-related issues.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a gynecologist or a vulvar specialist, to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the individual’s specific symptoms and medical history. Each person’s experience with vulvodynia is unique, so a personalized approach to treatment is essential for the best possible outcome.
MEDICATIONS
Several medications can be used to help manage the symptoms of vulvodynia. Keep in mind that the choice of medication and its effectiveness may vary depending on individual factors and the specific type of vulvodynia. Here are some common medications that may be prescribed:
- Topical Lidocaine or Lidocaine Cream:
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that can be applied directly to the vulvar area to provide temporary pain relief.
- Topical Steroids:
Steroid creams or ointments can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching or irritation in the vulvar region.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants:
Medications like amitriptyline or nortriptyline are often used at lower doses than those used for depression to help manage nerve-related pain and improve sleep.
- Anticonvulsants:
Certain anticonvulsant medications, such as gabapentin or pregabalin, are prescribed to help control nerve pain associated with vulvodynia.
- Selective Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs):
Medications like duloxetine may be used to manage chronic pain and improve mood.
- Calcium Channel Blockers:
These medications, such as nifedipine, can help relax blood vessels and may have pain-relieving effects.
- Hormone Creams or Hormone Therapy:
For vulvodynia related to hormonal imbalances, topical estrogen creams or hormone replacement therapy might be considered.
- Antihistamines:
In some cases, antihistamines may be used to reduce itching and inflammation in the vulvar area.
It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare professional when taking medications for vulvodynia. They will carefully assess your symptoms, medical history, and any potential interactions with other medications you may be taking. Additionally, some medications might take time to show their full effect, and adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary to achieve the best results.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions and report any side effects or changes in your symptoms during the course of treatment. If you have any questions or concerns about the medications prescribed, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
PREVENTATIVE MEASURES
There are some strategies and lifestyle choices that may help reduce the risk or severity of vulvodynia symptoms:
- Good Hygiene:
Maintaining proper hygiene in the vulvar area can help prevent infections and irritation that might contribute to vulvodynia. Avoid using harsh soaps, douches, or perfumed products and opt for gentle, unscented cleansers instead.
- Avoid Irritants:
Be mindful of potential irritants, such as certain fabrics, tight-fitting clothing, or scented hygiene products, and try to avoid them if they cause discomfort.
- Use Lubrication:
During sexual intercourse, using water-based lubricants can reduce friction and minimize discomfort, especially for women who experience pain during intercourse.
- Stress Management:
Chronic stress can exacerbate pain sensitivity, so practicing stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing may be beneficial.
- Communication with Partners:
Open communication with sexual partners about any discomfort or pain during intercourse is essential. It allows for understanding and support during intimate moments.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises:
Engaging in pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen the pelvic muscles and potentially reduce pain related to pelvic floor tension.
-
Regular Gynaecological Checkups:Regular visits to a gynaecologist for routine checkups can help identify and address any potential issues early on.
-
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can contribute to overall well-being.
It’s important to note that while these strategies may be beneficial in reducing the risk of vulvodynia or managing symptoms, there is no foolproof prevention method. If you experience any symptoms of vulvodynia or have concerns about your vulvar health, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health needs and concerns. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, vulvodynia is a condition characterized by chronic pain or discomfort in the vulvar area, affecting the external female genitalia. The exact causes of vulvodynia are not fully understood and may vary from person to person. Symptoms can include persistent pain, burning, stinging, itching, and sensitivity to touch. It may also lead to pain during sexual intercourse and other daily activities, impacting a person’s quality of life.
The treatment for vulvodynia involves a combination of approaches, such as topical medications, oral medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, hormone therapy, and counseling. Each individual’s experience with vulvodynia is unique, so a personalized approach to treatment is crucial for effective management.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of vulvodynia, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation and support from a healthcare professional specializing in women’s health or gynecology. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
10
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer