- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
Vaginal infections are conditions that result from an overgrowth of harmful microorganisms in the vaginal area. The vagina normally contains a balance of bacteria and other microorganisms that help maintain its health. However, certain factors can disrupt this balance, leading to an increased growth of harmful bacteria, yeast, or other pathogens, causing an infection. A vaginal yeast infection is an infection of the vagina that causes itching and burning of the vulva, the area around the vagina. They are. caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida.

Common types of vaginal infections include:
1. Yeast Infections:
These are caused by an overgrowth of Candida, a type of yeast normally found in the vagina. Symptoms may include itching, burning, thick white discharge, and redness or swelling around the vaginal opening.
2. Bacterial Vaginosis (BV):
BV occurs when there is an imbalance in the vaginal bacteria, with an overgrowth of harmful bacteria compared to the beneficial ones. Symptoms often include a thin, greyish-white discharge with a fishy odour and itching or irritation.
3.Trichomoniasis:
This is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Symptoms may include yellow-green vaginal discharge, vaginal itching, and discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse.
4. Vaginal Atrophy:
This is not an infection but rather a condition related to hormonal changes, typically seen during menopause. It causes thinning and inflammation of the vaginal walls, leading to dryness, itching, and pain during intercourse.
5. Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VVC):
Also known as recurrent yeast infections, this condition involves multiple episodes of yeast infections over time.
Treatment for vaginal infections depends on the specific type of infection. Over-the-counter or prescription antifungal or antibiotic medications may be prescribed to address the underlying cause and relieve symptoms. Maintaining good genital hygiene, avoiding douching, wearing breathable underwear, and practising safe sex can help prevent some types of vaginal infections. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
If you suspect you have a vaginal infection or experience any symptoms of discomfort or abnormal discharge, it’s essential to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Self-diagnosis and treatment without professional guidance may not effectively address the issue and may even worsen the condition.
SYMPTOMS WHILE SUFFERING FROM VAGINAL INFECTION?

Symptoms of a yeast infection may include:
- Itching:
Feeling an intense itchiness in and around the vagina is a common symptom of a yeast infection.
- Burning Sensation:
Some women may experience a burning sensation or discomfort in the vaginal area.
- Abnormal Discharge:
The vaginal discharge may become thicker, white, and clumpy, similar to cottage cheese.
- Redness and Swelling:
The skin around the vaginal opening might appear red and swollen.
- Pain During Intercourse and Urination:
Some women may feel pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse or urination.
CAUSES LEADING TO VAGINAL INFECTIONS
Vaginal infections can be caused by various factors that disrupt the normal balance of microorganisms in the vagina. Some common causes of vaginal infections include:
- Bacterial Imbalance:
The vagina normally contains a balance of good bacteria and harmful bacteria. When there is an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a decrease in beneficial bacteria, it can lead to conditions like bacterial vaginosis (BV).
- Yeast Overgrowth:
Yeast infections occur when there is an overgrowth of the Candida fungus, which is naturally present in the vagina. Factors such as hormonal changes, antibiotic use, or a weakened immune system can trigger yeast infections.
- Sexual Activity:
Certain sexual practices or having a new sexual partner can increase the risk of developing vaginal infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like trichomoniasis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia, and others.
- Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause can alter the vaginal environment, making it more prone to infections.
- Use of Antibiotics:
Taking antibiotics can disrupt the balance of vaginal bacteria, increasing the risk of yeast infections or BV.
- Douching:
Vaginal douching can disturb the natural balance of vaginal flora and may increase the risk of infections.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes:
High blood sugar levels can create an environment favorable for yeast overgrowth, leading to recurrent infections.
- Tight or Non-Breathable Clothing:
Wearing tight or non-breathable underwear or clothing can create a warm and moist environment, promoting the growth of harmful bacteria or yeast.
- Weakened Immune System:
Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV, certain medications, or chronic illnesses, can make the body more susceptible to infections.
- Vaginal Irritants:
Use of scented soaps, feminine hygiene products, or strong detergents in underwear can irritate the vagina and increase the risk of infections.
It’s essential to remember that not all vaginal infections are caused by the same factors, and each type of infection may have specific risk factors. If you suspect you have a vaginal infection or experience any symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Proper identification of the cause can help guide the treatment and prevent future occurrences.
YEAST INFECTIONS & BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
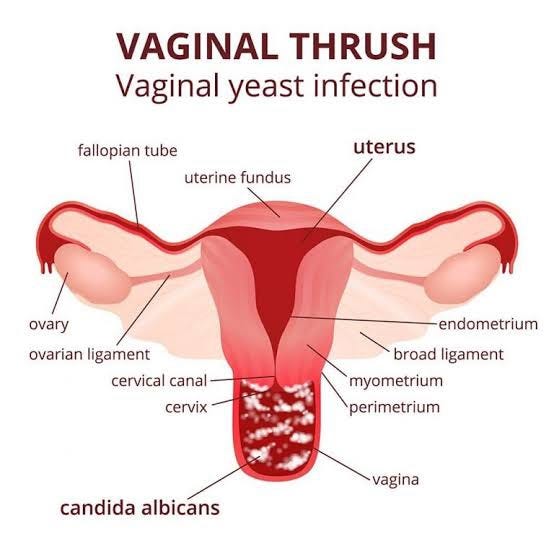
YEAST INFECTIONS
Yeast infections are not typically serious, but they can be uncomfortable and bothersome. They are not considered sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as yeast naturally exists in the body. However, sexual activity can sometimes lead to the transfer of yeast between partners.
Yeast infections can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Antibiotic use, which can disrupt the normal balance of bacteria in the vagina.
- Hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or menstruation.
- Weak immune system.
- Diabetes or high blood sugar levels.
- Tight-fitting or non-breathable clothing.
- Moist environments, like staying in wet swimsuits or sweaty workout clothes for too long.
Fortunately, yeast infections can often be treated with over-the-counter antifungal creams or suppositories. In more severe or recurrent cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger antifungal medications. It’s essential to follow the treatment as directed and complete the full course, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
To prevent yeast infections, maintain good genital hygiene, avoid douching, wear breathable underwear made of natural fabrics, and practice safe sex. If you suspect you have a yeast infection, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS
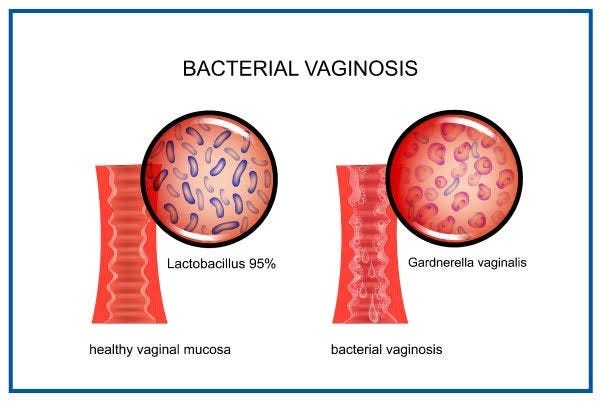
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection caused by an imbalance in the natural bacteria that normally live in the vagina. Normally, the vagina contains both good and harmful bacteria, and they usually coexist without causing problems. But in BV, there is an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, upsetting the natural balance.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis may include:
- Unusual Discharge:
The vaginal discharge may become thin, greyish-white, or milky with a fishy odour. The odour is often more noticeable after sexual intercourse or during menstruation.
- Itching or Irritation:
Some women may experience mild itching or irritation in the vaginal area.
- Burning Sensation:
There might be a mild burning sensation during urination or sexual intercourse.
BV is not a sexually transmitted infection (STI), but having multiple sexual partners or douching can increase the risk of developing it. It is essential to note that while BV can cause discomfort and inconvenience, it is usually not a serious health concern.
The exact cause of BV is not always clear, but it is linked to changes in the vaginal environment. Factors that can increase the risk of developing BV include douching, new sexual partners, and certain lifestyle habits.
Treatment for bacterial vaginosis usually involves antibiotics, either in the form of oral medication or vaginal gel or cream. Completing the full course of treatment is essential to ensure that the infection clears completely.
If you experience any symptoms of BV or suspect you may have an infection, it’s essential to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early treatment can help relieve symptoms and prevent complications. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
PREVENTATIVE MEASURES TO AVOID VAGINAL INFECTIONS
Preventing vaginal infections involves adopting healthy habits and making lifestyle choices that help maintain the natural balance of the vaginal environment. Here are some preventive measures to reduce the risk of vaginal infections:
- Practice Good Genital Hygiene:
Clean the genital area gently with mild, unperfumed soap and water. Avoid douching, as it can disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora and increase the risk of infections.
- Use Condoms:
Consistent and correct use of condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections ( STIs) that can cause vaginal infections.
- Limit Sexual Partners:
Reducing the number of sexual partners and having a mutually monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner can help lower the risk of STIs.
- Avoid Irritants:
Avoid using scented soaps, feminine hygiene products, or strong detergents on or around the genital area, as they can irritate the vagina and disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora.
- Wear Breathable Underwear:
Choose cotton underwear and avoid tight or non-breathable clothing, as they can create a warm and moist environment that promotes the growth of harmful bacteria or yeast.
- Manage Diabetes:
If you have diabetes, work with your healthcare provider to manage blood sugar levels effectively. High blood sugar can promote yeast overgrowth and increase the risk of infections.
- Limit Antibiotic Use:
Take antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow the prescribed course. Overuse of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of vaginal bacteria.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Eat a balanced diet, stay physically active, and manage stress to support overall health, including immune function and vaginal health.
- Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to help flush out toxins and support vaginal health.
- Regular Check-ups:
Attend regular gynaecological check-ups to monitor and maintain vaginal health. If you experience any symptoms of a vaginal infection, seek medical advice promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Being aware of the factors that increase your risk and adopting healthy habits can significantly contribute to reducing the risk of vaginal infections and maintaining overall vaginal health.
How common are vaginal yeast infections?
Up to 75% of women or people assigned female at birth (AFAB) will have at least one vaginal yeast infection in their life, and over half will get two or more in their lifetime. Yeast infections are the second most common cause of vaginitis (bacterial vaginosis is the most common).
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS!
Q: What is the difference between a yeast infection and bacterial vaginosis?
A: Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of the Candida yeast in the vagina, leading to itching, white, clumpy discharge, and discomfort. Bacterial vaginosis, on the other hand, is caused by an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina, resulting in a thin, greyish-white discharge with a fishy odor and irritation. While both are common vaginal infections, they have different causes and require different treatments.
Q: Can I get a vaginal infection from swimming pools or hot tubs?
A: It is uncommon to get a vaginal infection directly from swimming pools or hot tubs. However, spending time in these environments can create a warm and moist setting, which may increase the risk of vaginal infections. It’s essential to maintain good genital hygiene, change out of wet swimwear promptly, and avoid sitting in wet swimsuits for extended periods to reduce the risk of infection.
Q: Can a vaginal infection affect my ability to get pregnant?
A: In some cases, untreated vaginal infections like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can be caused by certain STIs, can lead to inflammation and scarring in the reproductive organs. This scarring can potentially affect fertility and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. It’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you have a vaginal infection to avoid potential complications.
Q: Can I treat a yeast infection with over-the-counter medication, or do I need to see a doctor?
A: Mild yeast infections can often be treated with over-the-counter antifungal creams or suppositories. However, if you are unsure about the cause of your symptoms or have recurrent infections, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Q: Is bacterial vaginosis a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
A: Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is not classified as an STI, but it can be associated with sexual activity. Having multiple sexual partners or a new sexual partner may increase the risk of developing BV. However, it can also occur in women who have never had sexual intercourse.
Q: Can I prevent all types of vaginal infections by practicing good hygiene?
A: While good genital hygiene is essential for maintaining vaginal health, it may not prevent all types of vaginal infections. Some infections, such as yeast infections and BV, can be influenced by various factors beyond hygiene, including hormonal changes, sexual activity, antibiotic use, and overall health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adopting other preventive measures, such as using condoms during sexual activity, can also help reduce the risk of some vaginal infections. If you have concerns about vaginal health or experience any symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, vaginal infections are common conditions that can affect women of all ages. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for effectively managing vaginal infections and preventing complications. If you experience any symptoms of a vaginal infection, such as itching, abnormal discharge, or discomfort, it’s essential to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional. Proper diagnosis is key to determining the appropriate treatment, whether it’s over-the-counter medication or prescription drugs. It should be noted, QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes Maintaining good genital hygiene, practicing safe sex, avoiding irritants, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the prevention of vaginal infections. Regular gynecological check-ups can also help monitor and maintain vaginal health. By being proactive about vaginal health and seeking timely medical attention when needed, women can take charge of their well-being and enjoy optimal reproductive and overall health.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer