- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
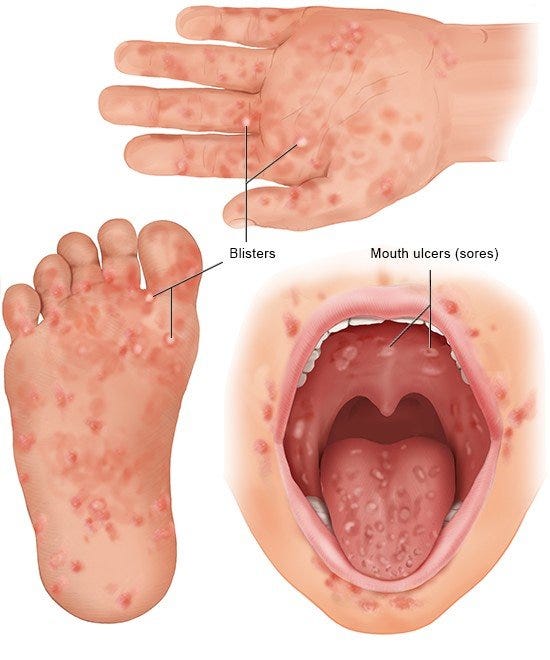
A. Definition of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a viral infection that primarily affects infants and young children. A group of enteroviruses, most frequently Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus 71, are responsible for its development. Fever, a sore throat, and malaise are some of the early symptoms of HFMD. On the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, and the inside of the mouth, they are typically followed by the appearance of visible, tiny, uncomfortable blisters or sores. The disease is primarily spread through direct contact with infected individuals, respiratory droplets, or contact with contaminated surfaces.. Although they are mostly minor and self-limiting, serious cases occasionally happen and necessitate immediate medical attention and supportive care.
B. Brief overview of its prevalence and affected populations
A common viral infection, Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) primarily appears in hot, humid climates. The majority of victims are infants and young children under the age of five, particularly those attending daycare centres, preschools, and schools where close contact encourages quick transmission. Although adults and teenagers can sometimes develop HFMD, their symptoms are frequently less severe than those of young children. HFMD has an impact on a large portion of Asia, including China, Singapore, Malaysia, and Vietnam as well as other nations like Australia and the US. While the majority of HFMD cases are moderate and self-resolve, it takes monitoring and public healthcare measures to stop outbreaks and properly treat severe cases.
Causes and Transmission
Identification of the viruses responsible for HFMD (Enterovirus types)
- Coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16): The most frequent cause of HFMD is CV-A16. It is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that is a member of the Enterovirus species A family. The majority of HFMD patients are caused by CV-A16, which often results in minor symptoms and a self-limiting course of the disease. Even while it is typically connected to milder cases, it can still cause discomfort and difficulties, particularly in young children.
2. Enterovirus 71 (EV71): EV71, a member of the Enterovirus species A, is another important contributor to HFMD. The neurological side effects of this virus include aseptic meningitis, encephalitis, and acute flaccid paralysis, as well as more severe cases of HFMD.
Multiple localities have reported severe EV71 outbreaks, raising worries for the public’s health.
Modes of transmission: direct contact, respiratory droplets, and contaminated surfaces
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is caused by a highly contagious virus that can spread in a variety of ways. The following are the main forms of transmission:
1. Direct Contact: Direct contact with an infected person is the most prevalent way that HFMD is communicated. The virus can be found infected people’s saliva, nasal secretions, blister fluid, and feces. Hugging, kissing, or engaging in other forms of close physical contact with an infected person can contribute to the virus’s ability to spread.
2. Respiratory Droplets: When an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, respiratory droplets containing the virus may be expelled into the air. If a susceptible person breathes in these droplets, they could catch the virus.
3.Contaminated Surfaces: Contact with contaminated objects and surfaces can also spread HFMD. The virus can remain on surfaces for several hours to days, depending on the environment. Before touching their faces, mouths, or eyes, people may come into contact with infected toys, doorknobs, or cutlery.
It’s essential to maintain good hygiene, which includes consistently washing your hands and sanitizing commonly touched surfaces, to reduce the chance of transmission and stop the development of HFMD.
Clinical Presentation
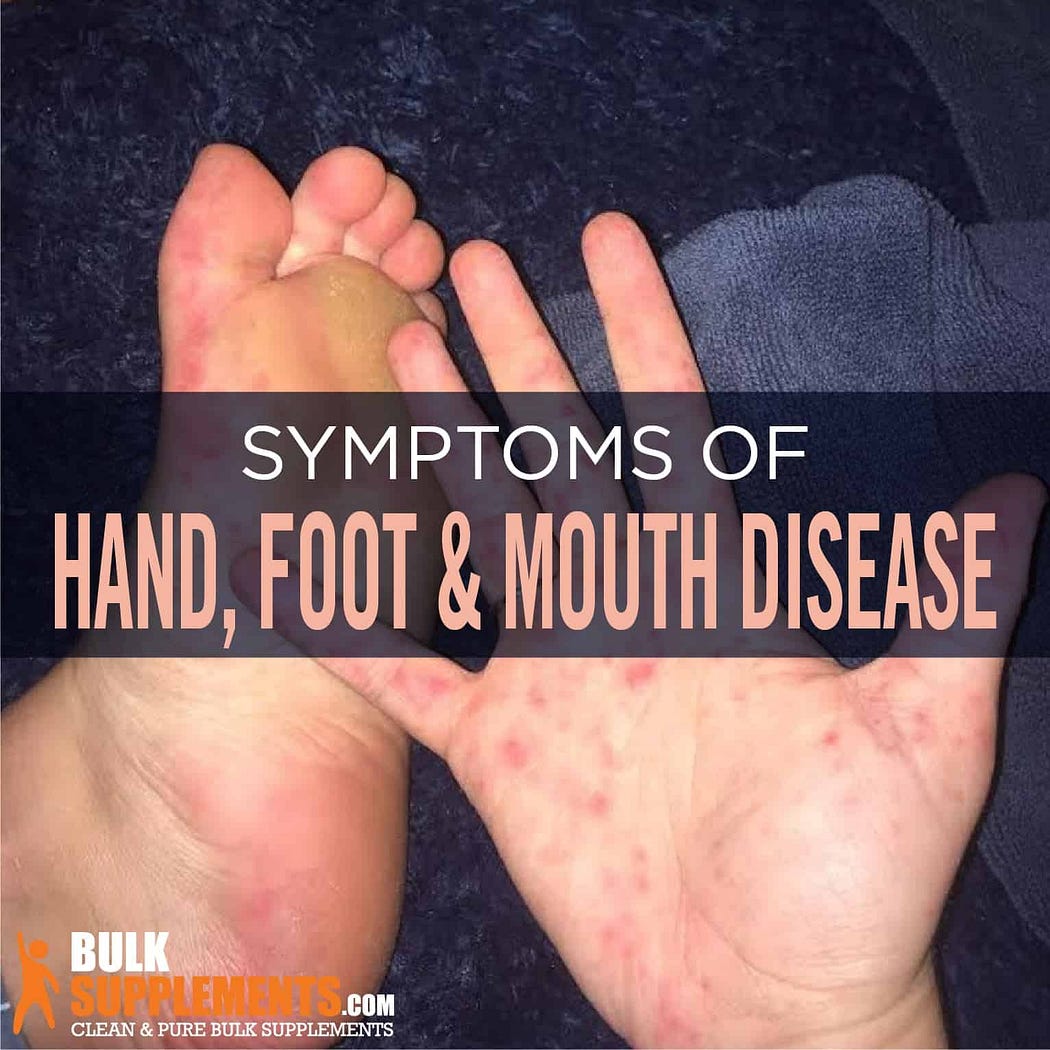
Fever, a sore throat, and malaise are early signs.
1.Fever: HFMD frequently starts with an abrupt onset of fever, which can range in severity from mild to moderate. One of the earliest obvious indicators of the infection, the fever typically lasts for many days.
-
Sore Throat: In addition to fever, HFMD sufferers may also feel sore throats. It might be uncomfortable to eat or drink because of the throat discomfort, which can range from mild to severe.
-
Malaise: HFMD can result in a general malaise that includes weakness, exhaustion, and discomfort all around. Patients may feel worn out and lifeless during the early stages of the illness.
Early diagnosis and medical examination are crucial to distinguish HFMD from other common viral illnesses since these early symptoms can be confused with other viral diseases.
Development of characteristic symptoms: lips, hands, and feet covered in blisters.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) evolves from the initial symptoms to the emergence of recognizable symptoms. Tiny, unpleasant blisters or sores begin to appear inside the mouth, on the palms of the hands, and on the bottoms of the feet. These can make eating and drinking uncomfortable and even difficult.
Potential complications and severe cases
Complications may occur in severe cases of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD). There could be neurological side effects such acute flaccid paralysis, encephalitis, or aseptic meningitis. These difficulties could develop into more significant health problems and demand urgent medical care. However, severe cases are quite uncommon, and the majority of patients make a full recovery without any issues.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
The main components of the Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) diagnosis are clinical assessment and physical examination. Identification of HFMD is aided by the typical symptoms of fever, sore throat, and the appearance of tiny blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth. Enteroviruses can be confirmed by laboratory tests, such as viral culture from throat swabs or stool samples. To differentiate HFMD from other viral illnesses with comparable symptoms, such as herpangina, chickenpox, and strep throat, differential diagnosis is essential. A correct diagnosis is necessary to guarantee adequate therapy, stop the disease from spreading, and provide supportive care to alleviate symptoms.
Prevention and Control
Public health initiatives and good hygiene habits are the main components of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) prevention and control efforts. Transmission can be avoided with regular handwashing, good respiratory care, and appropriate disinfection of infected surfaces. Outbreaks can be controlled by quarantining close contacts and isolating affected people. Vaccination against Enterovirus 71 in some areas has showed promise in lessening the severity of infections, despite the fact that there is no particular vaccine for HFMD. Early epidemic detection and management depend heavily on public health surveillance and awareness initiatives.
Supporting preventative and control initiatives is made possible by the Qme Healthcare Software System. Due to its extensive data management capabilities, HFMD cases can be efficiently tracked and monitored by healthcare providers. Rapid information interchange between healthcare facilities is made possible by the program, enabling early detection of outbreaks and fast application of preventive measures. The integrated reporting and analytics feature of Qme Healthcare Software System also help health authorities analyse epidemiological patterns, direct targeted interventions, and guarantee a coordinated response to HFMD outbreaks. [Qme Healthcare Software System- https://www.qme.co.in/info/hospital-info-systems dramatically improves the efficacy of HFMD prevention and control efforts, resulting in better public health outcomes. It does this by improving communication and data administration.
Treatment and Management
Supportive care is the mainstay of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) treatment and hospital management. This involves taking action to reduce the temperature, discomfort, and agony brought on by mouth sores and blisters. Hydration is important, especially if eating is challenging because of oral lesions. Hospitalization and specific medical procedures may be required in severe cases with neurological consequences. Although their normal use is still debatable, antiviral drugs may be taken into consideration in some circumstances. For effective management and outbreak containment, HFMD cases must be quickly identified and reported.
The Qme Healthcare Software System enhances data interchange and communication among healthcare practitioners, which is essential for treatment and administration. Due to its real-time tracking of HFMD cases, possible epidemics can be identified early, allowing for prompt action. The software’s integrated reporting and analytics features also help health authorities track disease patterns, make resource allocation easier, and guarantee the best possible patient care. Qme Healthcare Software System. improves communication between medical facilities, maximizing management and treatment plans for better HFMD results.
VII. Impact on Public
Public health may be significantly impacted by Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD). HFMD outbreaks can spread quickly, especially in environments with young children, such schools and childcare facilities. The illness may result in higher healthcare costs and financial burdens. Controlling HFMD and lessening its effects on affected populations depend heavily on public health initiatives, such as surveillance, early detection, and preventive treatments. To lessen the intensity and frequency of HFMD outbreaks and protect the public’s health, health authorities must rigorously endeavour to raise awareness among the population, put preventive measures into place, and ensure prompt case management.
VIII. Conclusion
Finally, it should be noted that Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a widespread and incredibly contagious viral infection that mostly affects babies and young children. Early diagnosis of symptoms and appropriate preventative measures are essential for controlling outbreaks and reducing their negative effects on public health. By improving communication, enabling real-time data interchange, and enhancing surveillance efforts, the Qme Healthcare Software System. plays a crucial part in HFMD management. Health authorities may effectively allocate resources, track illness patterns, and respond to epidemics thanks to its integrated reporting and analytics capabilities. The [Qme Healthcare Software System]enter link description here. greatly contributes to limiting the spread and effects of HFMD, hence improving overall public health outcomes, by optimizing treatment and preventive efforts.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer