- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer
EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
EXPLORING BENEATH THE SURFACE: UNDERSTANDING BARTHOLIN CYSTS AND ABSCESSES
INTRODUCTION
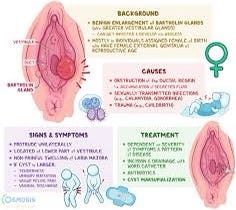
A Bartholin’s cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can develop near the opening of the vagina. It forms when the Bartholin’s gland, which is responsible for producing lubricating fluid for the vagina, becomes blocked. This blockage can cause a buildup of fluid, resulting in the formation of a cyst. If the cyst becomes infected, it can lead to the development of a Bartholin’s abscess. An abscess is a painful, swollen lump that forms when bacteria enter the blocked gland and cause an infection.
Both cysts and abscesses can cause discomfort, pain, and swelling in the genital area. Treatment options may include warm compresses, drainage of the abscess, antibiotics for infection, or in some cases, surgical intervention. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment if you suspect you have a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess.
CAUSES
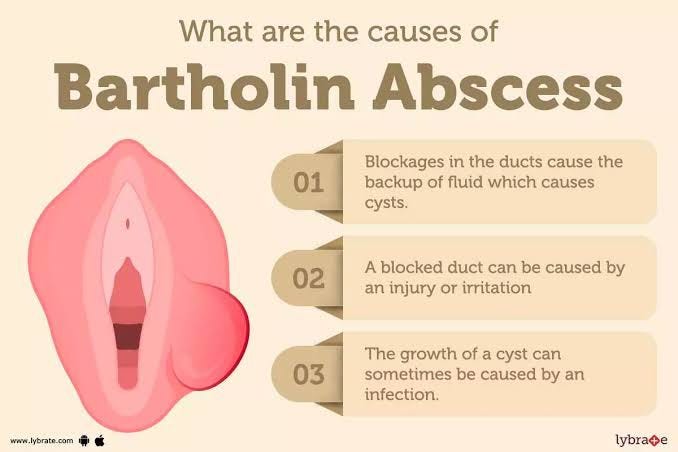
The causes of Bartholin’s cysts and abscesses are related to the blockage of the Bartholin’s gland, which is responsible for producing lubricating fluid for the vagina. Here are some common factors that can contribute to the development of Bartholin’s cysts and abscesses:
- Blockage:
The most common cause is a blockage of the Bartholin’s gland duct. This can prevent the gland’s secretions from flowing out, leading to the accumulation of fluid and the formation of a cyst.
- Bacterial Infection:
If bacteria enter the blocked gland, it can cause an infection. This infection can result in the formation of an abscess, which is a painful lump filled with pus.
- Inflammation:
Inflammation of the Bartholin’s gland or its duct can contribute to blockages and cyst formation.
- Hormonal Changes:
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those that occur during menstruation or pregnancy, can affect the gland’s secretions and potentially lead to cyst development.
- Sexual Activity:
Engaging in sexual activity can sometimes cause friction and irritation that leads to inflammation and subsequent cyst formation.
- Poor Hygiene:
Inadequate genital hygiene can increase the risk of bacterial growth and infection.
- Skin Conditions:
Certain skin conditions or diseases that affect the genital area can contribute to the development of cysts or abscesses.
- Injury or Trauma:
Trauma or injury to the vaginal area can disrupt the normal functioning of the Bartholin’s gland, leading to blockages and cyst formation.
It’s important to note that while these factors can increase the likelihood of Bartholin’s cysts and abscesses, the exact cause can vary from person to person. If you suspect you have a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess, it’s recommended to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. To make the treatment more feasible, QMe is a cutting-edge hospital management software designed to revolutionize healthcare facilities worldwide. With its intelligent queue-based OPD management system, patients experience reduced waiting times and optimized appointment scheduling. The software’s comprehensive patient history and electronic health records ensure seamless access to critical medical information, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and provide personalized care. QMe’s automatic workflows streamline administrative tasks and treatment plans, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing human errors. The software’s IPD management feature enables smooth inpatient care coordination, while its TPA support simplifies insurance processes.
SPOTTING THE SIGNS OF BARTHOLIN’S CYST AND ABSCESS
The symptoms of Bartholin’s cyst and abscess can vary in severity, but they generally involve discomfort and swelling in the genital area. Here are common symptoms associated with these conditions:
Bartholin’s Cyst:
-
Small Lump: You might notice a painless, small lump near the vaginal opening.
-
Discomfort: While the cyst itself might not be painful, you could experience discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the genital area.
-
Redness and Swelling:The area around the cyst might become red, swollen, and tender.
-
Mobility: The lump might be mobile and easily felt with your fingers.
Bartholin’s Abscess:
-
Pain: An abscess is often accompanied by pain that can range from mild to severe. The pain might worsen with movement or pressure.
-
Swelling: The area around the abscess can become significantly swollen and tender.
-
Redness: The skin over the abscess might appear red and inflamed.
-
Fever: In some cases, an abscess can cause fever and general feelings of illness.
-
Pus Drainage: If the abscess ruptures, it can release pus and provide temporary relief, but the infection might still require medical attention.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess. While some cysts might resolve on their own, abscesses usually require medical intervention to prevent complications and manage the infection. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the severity of your symptoms. Additionally, QMe offers packages support for various medical services and features automated billing to ensure transparent and hassle-free financial transactions. Embracing QMe empowers hospitals to enhance patient experiences, optimize healthcare workflows, and deliver top-notch medical services.
TREATING THE TROUBLE

The treatment for Bartholin’s cyst and abscess depends on the severity of the condition and whether an infection is present. Here are common treatment options:
Bartholin’s Cyst:
- Warm Compresses:
Applying warm compresses to the cyst can help promote drainage and relieve discomfort. This might encourage the cyst to resolve on its own.
- Sitz Baths:
Soaking in a warm bath (sitz bath) can also help promote drainage and alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes:
Staying hydrated and practicing good genital hygiene can assist in preventing future cysts.
- Medical Monitoring:
If the cyst is small and not causing significant discomfort, a healthcare professional might recommend monitoring its progress.
Bartholin’s Abscess:
- Incision and Drainage:
If the abscess is causing pain and discomfort, a healthcare provider can perform a minor surgical procedure to make an incision and drain the pus.
- Antibiotics:
If an infection is present, antibiotics might be prescribed to treat the infection and prevent its spread.
- Word Catheter:
In some cases, a small catheter might be inserted into the abscess site to keep it open and allow continuous drainage.
- Marsupialization:
This surgical procedure involves creating a small incision and stitching the edges to the skin, allowing continuous drainage and reducing the likelihood of recurrence.
Surgical procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia, and recovery times vary depending on the specific treatment. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for post-treatment care to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications.
If you suspect you have a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess, it’s recommended to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess your condition, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the most appropriate treatment based on your individual situation.
MARSUPIALIZATION
Marsupialization is a surgical procedure used to treat certain types of cysts, including Bartholin’s cysts and some other cystic lesions. The goal of marsupialization is to create a permanent opening in the cyst, allowing for continuous drainage and preventing the cyst from reoccurring. Here’s an overview of the procedure:
- Procedure Overview:
. During marsupialization, a surgeon makes an incision into the cyst or abscess. Instead of stitching the incision closed, the edges of the incision are sewn to the surrounding skin, creating a small “pocket” or pouch. This pouch serves as a continuous drainage channel, allowing any accumulated fluid or pus to drain out naturally.
- Benefits:
. – Prevents the cyst from re-forming by maintaining a permanent drainage opening.
. – Reduces the risk of infection and abscess formation.
. – Minimizes discomfort and swelling associated with the cyst.
- Recovery
. – Recovery time can vary depending on the size and location of the cyst or abscess.
. – After the procedure, there might be some discomfort and swelling, which can be managed with pain relievers and following the surgeon’s post-operative instructions.
. – The surgical site needs to be kept clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Follow-up:
. – Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are typically scheduled to monitor the healing process and ensure that the cyst remains drained.
. – In most cases, the pouch created during marsupialization gradually closes on its own as the healing progresses.
It’s important to note that marsupialization is not always the appropriate treatment for all cases of cysts or abscesses. The decision to perform marsupialization or another treatment method is determined by the healthcare provider based on the individual’s specific condition, overall health, and other relevant factors.
If you’re considering or have been recommended for marsupialization, it’s crucial to consult a qualified healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and to discuss the procedure’s benefits, risks, and expected outcomes.
MEDICATIONS
For Bartholin’s cysts and abscesses, medication might be prescribed as part of the treatment plan. Here are some medications that healthcare professionals might use to manage these conditions:
Pain Relief:
. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with cysts or abscesses.
- Antibiotics:
. – Prescription Antibiotics: If the abscess is infected, your healthcare provider might prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. It’s important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
- Topical Creams:
. – Antibacterial Creams: In some cases, topical antibacterial creams might be recommended to prevent infection or promote healing after drainage of an abscess.
It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance when taking any prescribed medication. Be sure to inform your provider about any allergies, medical conditions, or other medications you might be taking to avoid potential interactions or complications.
Remember that medication is often used in conjunction with other treatment methods, such as warm compresses, incision and drainage, or other surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition. Your healthcare provider will determine the most suitable treatment plan based on your individual case.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, Bartholin’s cysts and abscesses are conditions that affect the Bartholin’s gland near the vaginal opening. While cysts form due to blockages in the gland’s ducts, abscesses develop when an infection occurs within a blocked gland. Both conditions can lead to discomfort, pain, and swelling in the genital area.
Treatment options vary based on the severity of the condition. For cysts, warm compresses, sitz baths, and lifestyle changes might be recommended. In cases of abscesses, surgical procedures like incision and drainage, antibiotics, and other interventions might be necessary to alleviate pain, drain pus, and treat infections.
If you suspect you have a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess, seeking prompt medical attention is advised. A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your individual needs, ensuring your comfort and overall well-being.
- “Empowering Emergency Medicine Physicians”
- “Queue Management Software and Hospitalists in Modern Healthcare”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Infectious-Disease-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Geriatric-Care”
- “Optimizing-Patient-Care-in-Pediatric-Rheumatology”
- “Pediatric-Pulmonology-Care”
- “Revolutionizing-Pediatric-Gastroenterology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Neurology-Care”
- “Optimizing-Pediatric-Cardiology”
- “Enhancing-Pediatric-Endocrinology-Care”
- “Empowering-Neonatologists-with-EMR-Software”
- “Pediatrics-in-Focus”
- “Empowering-Neurologists-with-Electronic-Prescriptions”
- “Streamlining-Dermatology-Practice”
- “Streamlining-Psychiatry-Practice”
- “A-Game-Changer-for-Infectious-Disease-Specialists”
- “Allergist/Immunologist-Practices-with-QME-EMR-and-Hospital-Management-Systems”
- “Empowering-Hematologists-and-Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-with-HMIS”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-with-Endocrinologist”
- “Healthcare-Management-with-QMe-EMR-for-Nephrologists”
- “Revolutionizing-Healthcare-Management-with-Cardiologist”
- “Streamlining-Operations-with-Queue-Management-Software”
- “Optimizing-Healthcare-Delivery”
- “Transforming-Healthcare-Management”
- HMIS And Decision Support Systems
- Dengue Unveiled: An Overview of Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention.
- Dengue Fever: Unraveling the Mosquito-Borne Menace.
- HMIS-and-Continuity-of-Care
- Project-Management-for-Successful-HMIS
- Catalysts of Wellness: The Transformative Power of Diagnosis and Screening in Healthcare
- Patient-Data-Management
- Guardians of Healthcare: The Vital Role of Fraud Detection in Ensuring Ethical Care
- Unlocking Insights
- Healthcare in the Digital Age: The History Of Development Of HMIS
- Transforming Healthcare
- Safeguarding-HMIS-Data
- HMIS-Integration-Challenges
- ANXIETY UNVEILED: CONQUERING FEARS AND CULTIVATING CALM.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- BEYOND THE BLUE: EMBRACING LIGHT ON THE PATH OF DEPRESSION.
- HMIS and Resource Allocation
- HMIS Data Accuracy and Integrity
- SOOTHING THE SILENT PAIN: UNDERSTANDING VULVODYNIA.
- Impact of HMIS on OPD Operations
- In Patient Management Through Health Management
- WITHIN THE SHADOWS: UNDERSTANDING BRAIN TUMOURS FROM WITHIN
- HMIS-and-Health-Insurance-Integration
- HMIS-Data-Analytics-for-Preventive-Care
- SILENT INTRUDERS: UNRAVELLING THE MYSTERIES OF PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
- BREAKING FREE: OVERCOMING THE HURDLE OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
- “HMIS and Doctor-Patient Communication”
- HEALING INSIGHTS: THE POWER OF THE HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM.
- SOLVING THE OVARIAN PUZZLE:UNDERSTANDING OVARIAN CYST INSIDE OUT
- Usability And User Experience In HMIS
- WARRIOR’S BATTLE: TRIUMPHING OVER UTERINE CANCER
- POLYCYSTIC OVARY PUZZLE: UNRAVELLING THE ENIGMA OF PCOS
- Unlocking-the-Potential-of-HMIS-Data-for Medical-Research-and-Healthcare-Policy-Enhancement
- Feminine Health Unplugged: Empowering Women in Vaginal Infection Awareness
- Revitalizing Feminine Comfort: A Journey Through Vaginal Wellness.
- HMIS Vendor Selection Guide
- UNDERSTANDING FIBROIDS: NAVIGATING THE INTRICACIES OF UTERINE HEALTH.
- Best Practices for Data Migration in Healthcare Management Information Systems (HMIS)
- CONCEIVING HOPE: NAVIGATING THE JOURNEY OF INFERTILITY
- MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES: CAUSES AND TREATMENT
- RISING ABOVE: EMPOWERING WOMEN WITH PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
- Leveraging HMIS for Enhanced Public Health Management and Disease Surveillance
- Challenges and Benefits of Implementing HMIS in Rural and Remote Healthcare Settings
- Securing Healthcare Continuity
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Bladder Cancer
- Skin Cancer (Melanoma)
- COLORECTAL CANCER
- All about Prostate Cancer
- Fighting out the Disease of Lung Cancer
- Advances in Breast Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- EHR SYMPHONY: HARMONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH ELECTRONIC RECORDS .
- Understanding Testicular Cancer: Detection, Treatment And Awareness.
- Childhood Obesity
- Kawasaki Disease
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Understanding Bone Cancer: A Brief Overview.
- Virtual Healing: Navigating Healthcare Through Telemedicine and Telehealth.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- PELVIC PAIN:CAUSES SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIONS
- Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Battling Pneumonia: Unveiling the Stealthy Invader of the Lungs
- Unravelling the Complexity of Allergic Reactions: Understanding, Managing, and Thriving
- Rashes (Eczema, Dermatitis)
- UNDERSTANDING CERVICAL DYSPLASIA: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND MANAGEMENT
- Chicken Pox
- Endometriosis Unmasked: A Closer Look at the Silent Struggle
- Croup
- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)
- THE DAWNING OF A NEW ERA: EMBRACING THE JOURNEY OF MENOPAUSE
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Strep Throat (Streptococcal Pharyngitis)
- Understanding Otitis Media(Ear Infection)
- 28th July In medical history!!
- Influenza (Flu) - Symptoms, Prevention and Management
- 27th July In medical history!!
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- SIGNIFICANCE AND ADVANTAGES OF HMIS: A DETAILED ANALYSIS
- Beyond Boundaries: Transforming Healthcare with Virtual Reality
- TRACK YOUR LIFE : A DETAILED UNDERSTANDING ON HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM
- GUARDING GUT HEALTH: YOUR GUIDE TO POTENTIAL CROHN’S DISEASE PREVENTION.
- PATHWAYS OF HOPE: NAVIGATING THE CHALLENGES OF ESOPHAGEAL CANCER
- Gastric Battles: Confronting Stomach Cancer Head-On.
- HMIS IN SMALL CLINICS: A STEP TO A BETTER FUTURE
- Harmonizing Your Cycle: A Journey to Menstrual Health and Balance.
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- GUARDING OUR INTIMATE WORLD: A CLOSER LOOK AT STI
- Real-World HMIS Implementation Case Studies: Using Data to Transform Healthcare
- Gastroenteritis (Stomach Flu)
- Asthama - The Anatomy Of Breathing
- Influenza - A Silent Intruder
- Breast Cancer